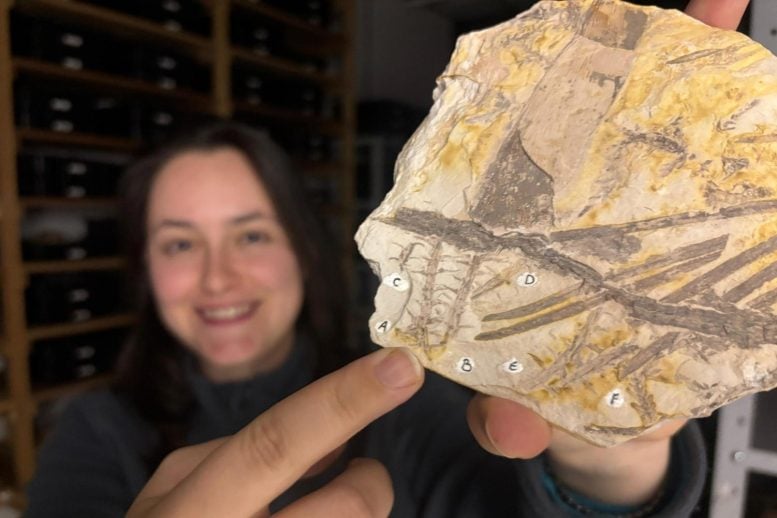
Scientists recognized a brand new plant genus, Franscinella, from a 296-million-year-old fossil in Brazil. The discover sheds gentle on historic plant evolution.
Brazilian paleobotanists have resolved a long-standing thriller by means of the redefinition of a fossil plant first described a long time in the past in southern Brazil. Their work has led to the institution of a brand new genus, Franscinella, to categorise the species now named Franscinella riograndensis (Salvi et al.) Carniere, Pozzebon-Silva, Guerra-Sommer, Uhl, Jasper et Spiekermann comb. nov.
This research forms part of the master’s thesis of Júlia Siqueira Carniere, now a doctoral student in the Graduate Program in Environment and Development at Univates (PPGAD). The study, published in the Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology, reexamines material once identified as Lycopodites riograndensis and provides the first confirmed record of lycopodites with in situ spores from the Permian strata of the Paraná Basin.
The finding not only updates the plant’s taxonomy but also addresses a scientific challenge that had remained unsolved for over 50 years: the documentation of in situ plant spores preserved in Upper Paleozoic clastic rocks (dating from 298.9 million to 252.17 million years ago) in Brazil. This breakthrough was made possible by the fossil’s exceptional preservation and the use of advanced microscopic techniques, combined with interdisciplinary collaboration across leading Brazilian research institutions.
A new look at a classic fossil
The species Lycopodites riograndensis was originally identified based only on broad external features seen in the fossil, such as the overall shape and arrangement of its stems. These early descriptions, made decades ago, lacked more detailed anatomical and spore-level information, which limited the accuracy of its classification.
With modern advances in microscopic sample preparation and imaging, a team from the University of Vale do Taquari – Univates, working within the Graduate Program in Environment and Development (PPGAD), revisited the original fossil material preserved in the Univates Paleontological Collection. Their goal was to determine whether newer, more refined techniques could reveal anatomical and palynological details that had not been previously observed.
The researchers applied a combination of scanning electron microscopy (SEM), vinyl polysiloxane silicone molding (VPS), and transmitted light microscopy. These tools made it possible to view both surface features and internal structures at high magnification and resolution. This analysis uncovered several characteristics that supported a taxonomic reclassification: isotomic branching of stems, a hallmark of certain fossil lycopsids; preserved tracheids in the vascular cylinder, crucial for identifying extinct plant groups; and trilete spores with verrucate ornamentation, found preserved in situ within the reproductive organs of the plant.
Securing spores in their original position (in situ) proved to be one of the most challenging yet decisive aspects of the study. Success came through the facilities of the itt Oceaneon Technological Institute at the University of Vale do Rio dos Sinos (Unisinos), which specializes in recovering microfossils such as spores, pollen, and marine microorganisms like ostracodes and radiolarians. The itt Oceaneon team applied a specialized recovery protocol, which turned out to be highly effective for this type of fossil material.
From micro to macro: connecting fossil records
The spores found in Franscinella riograndensis show morphology compatible with the palynological genus Converrucosisporites, common in Permian deposits in the Paraná Basin. This correspondence is relevant because it directly links the macrofossil record (visible parts of the plant) to the microfossil record (spores and pollen grains), broadening our understanding of past vegetation and ecosystems.
In practice, this means that researchers can now make more complete interpretations of Permian plant communities, integrating information from different lines of evidence. In addition, this correlation contributes to biostratigraphy studies, which use fossils to date and correlate rock layers.
Why is this discovery important?
The redefinition of Franscinella riograndensis shows how revisiting known fossils with new tools can generate groundbreaking discoveries. Many fossil groups, such as lycopodids, have historically been classified under broad, generic genera, in this case Lycopodites. This type of umbrella classification was a practical solution in the absence of more detailed information, but tends to be revised when new data becomes available.
From a paleobotanical point of view, the recording of lycopsids with spores in situ in the Paraná Basin opens up new perspectives for reconstructing the flora of the Permian and for understanding the evolution of vascular plants. From a global scientific perspective, this study contributes to the understanding of the diversity and distribution of herbaceous lycopsids during the Permian in Gondwana, being only the fifth known record, which makes this type of occurrence rare. In addition, it allows comparisons with similar records in other regions of the world, offering new data on the evolution and ecology of these plant groups in the Paleozoic.
Reference: “Franscinella riograndensis (Salvi et al.) gen. nov. et comb. nov.: The first record of a lycopsid with in situ spores for the Permian strata of the Paraná Basin, Brazil” by Júlia Siqueira Carniere, Ândrea Pozzebon-Silva, Rafael Spiekermann, Lilian Maia Leandro, Margot Guerra-Sommer, Dieter Uhl and André Jasper, 27 June 2025, Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology.
DOI: 10.1016/j.revpalbo.2025.105401
Never miss a breakthrough: Join the SciTechDaily newsletter.














